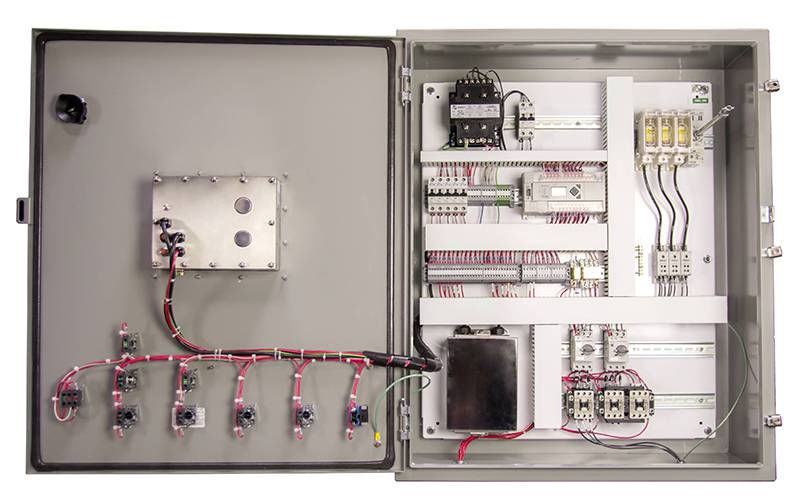
We Build Control Panels
US Systems is a Full-Service Panel Shop
We have talented industrial controls engineers on-staff ready to serve your needs.
Our systems feature industrial-duty control panels that automate much of the process, allowing your system to run smoothly, with less downtime.
We build control panels to meet your application needs and may include:
- NEMA-Rated Panels
- Disconnect Switch
- Primary Circuit Protection
- Industrial-Duty Buttons, Selector Switches, and Door Devices
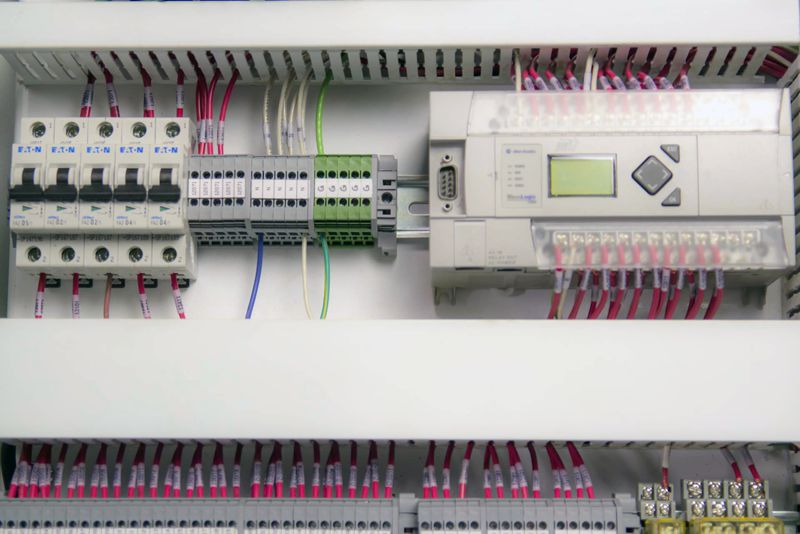
- PLC – Programmable Logic Controller
- Motor Starters
- HMI – Human Machine Interface
- LED Indicator Lights
- Variable-Speed Controls
- Touchscreen
- Remote Networking Capability
- Data Collection
Types of Control Panels
We’re passionate about constructing top-quality industrial control panels. We offer a wide-range of panels including:
- Motor Control Center
- PLC Control Panels
- VFD Control Panels
- HIM Panels
- Operator Stations
- Pneumatic Control Panels
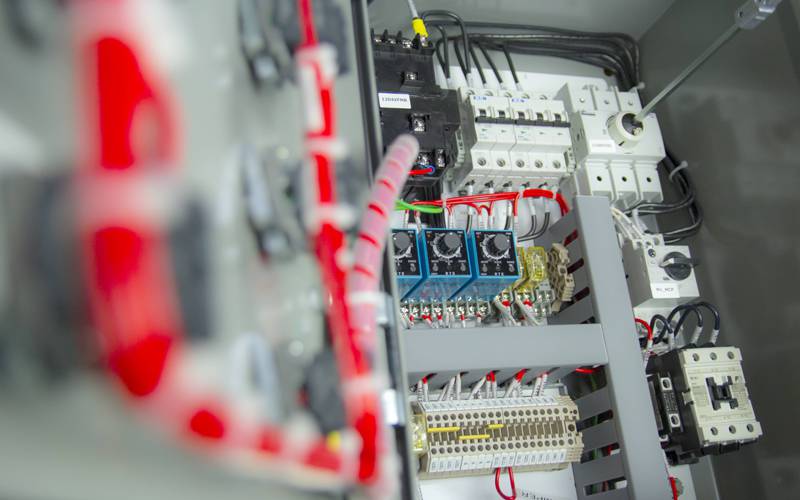
MCC
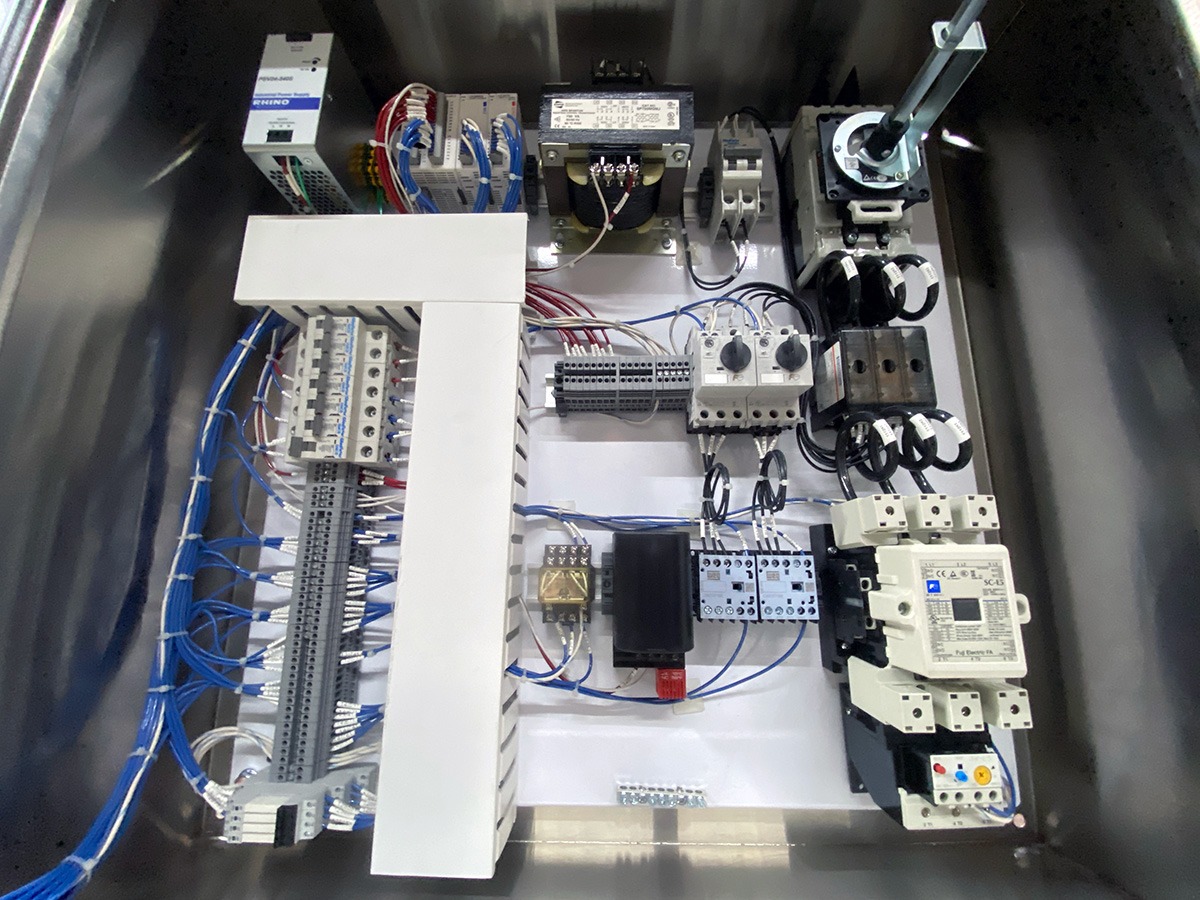
MCC’s contain power distribution busbar and mounting locations for motor controllers. Each motor controller contains a contactor or motor starter, as well as an overload relay for protecting the motor. They also have circuit protection devices such as a circuit breaker and fuses, and a power disconnect switch. They can also contain other components such as PLCs, VFDs, pushbuttons, indicator lights, and metering devices.
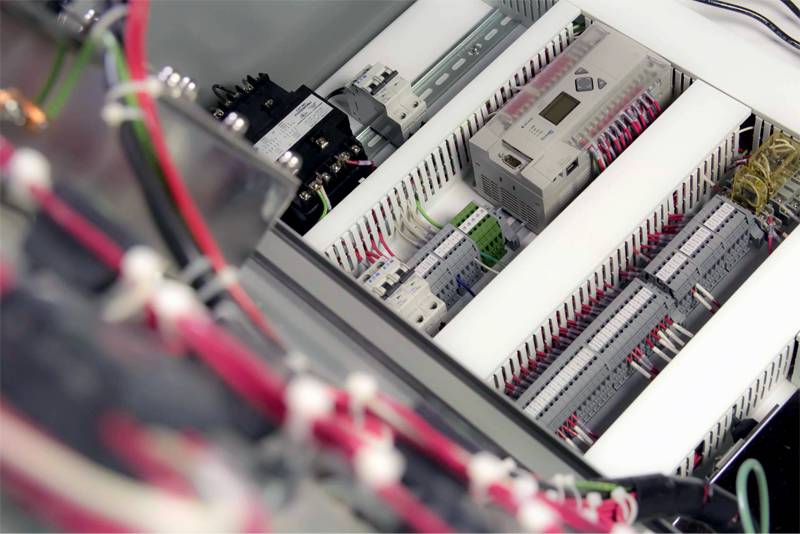
PLC Control Panels
A PLC control panel houses a PLC which is an industrial computer that receives input and sends output to devices such as valves, scales, motors, sensors, etc. This type of control panel houses the PLC and the necessary components to distribute power and protect electrical circuits. You might also find an ethernet switch to connect the PLC to a computer network, HMI, or other networked devices.
VFD Control Panels
VFDs are motor controllers that are able to vary the input of frequency and voltage. They can also control motor ramp-up and ramp-down during starting and stopping. This can improve efficiency, reduce energy consumption, or match the speed of the motor to process requirements. This panel can house single or multiple VFDs as well as power distribution components, circuit protection, motor protection devices, harmonic filters, PLCs etc.
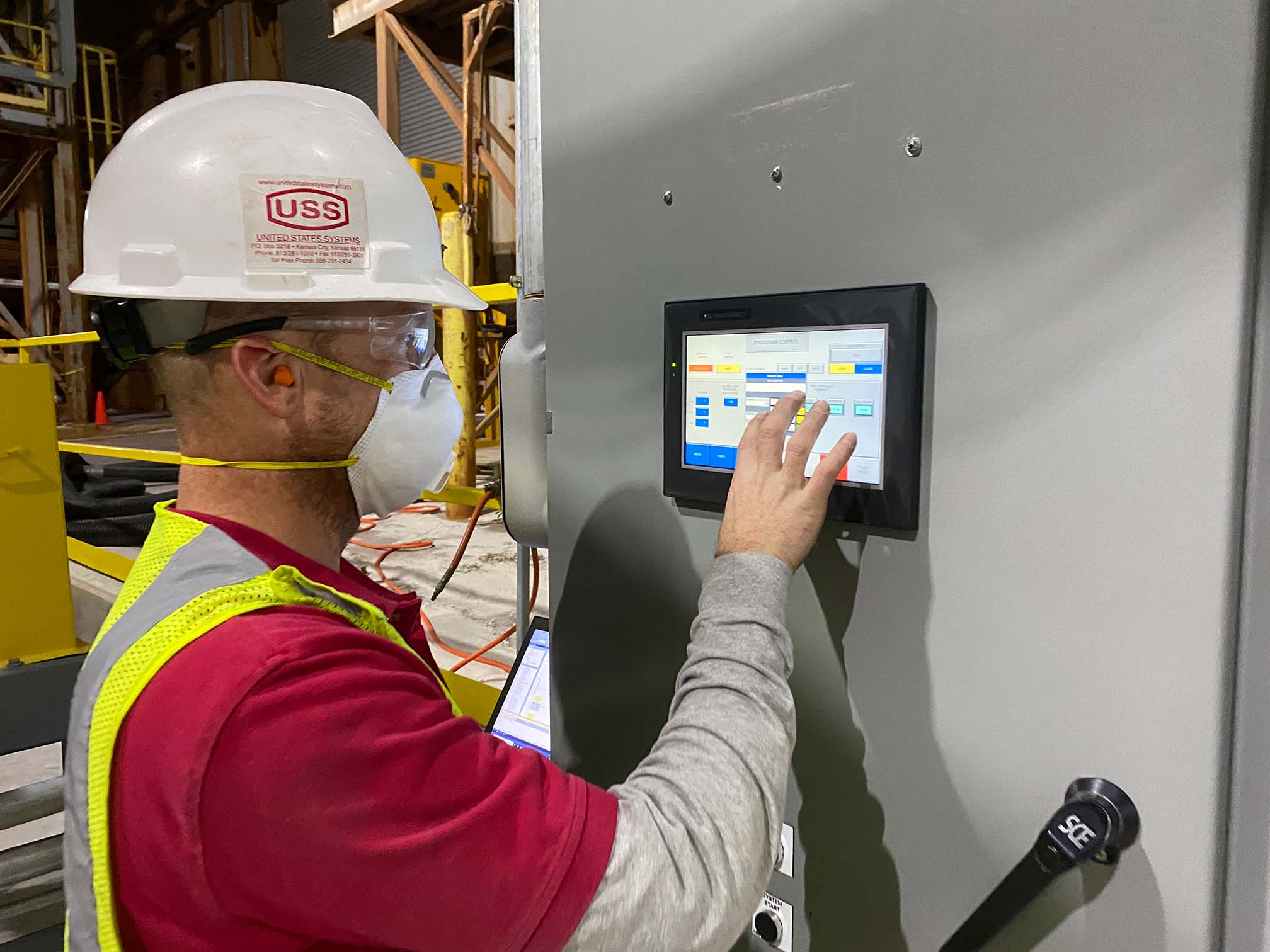
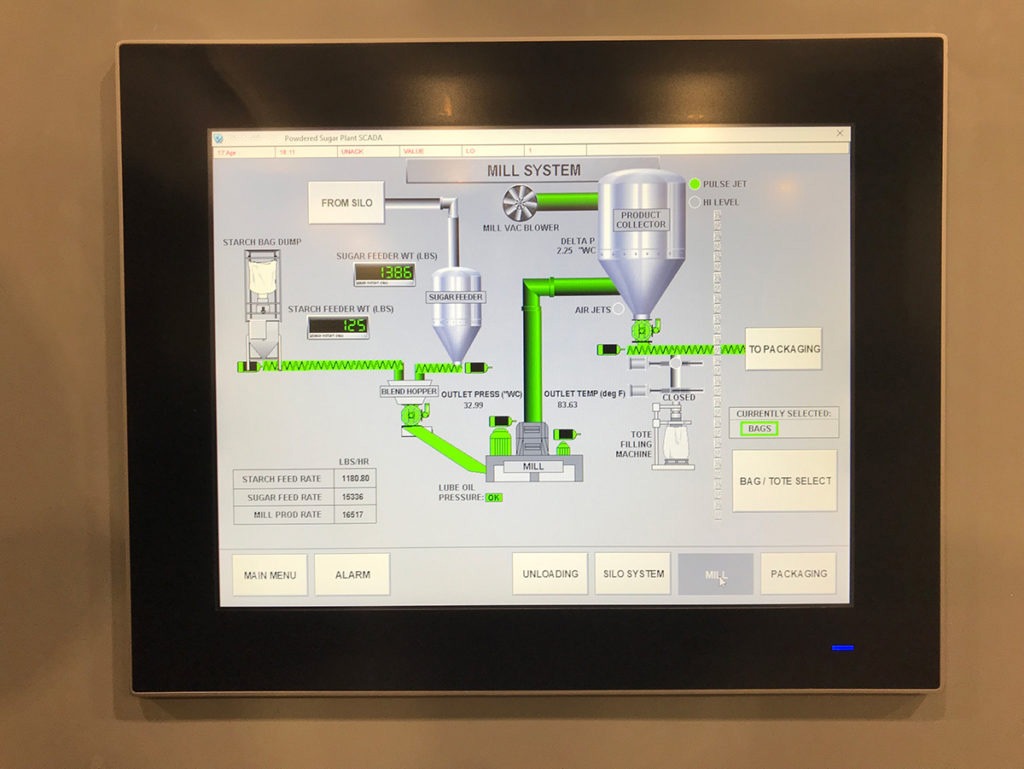
HMI Panels – Operator Stations
These panels will contain a display with a visual representation that allows operators to interact with and execute commands with the system. HMIs are often found in standalone enclosures near a machine, or located in the door of a control panel.
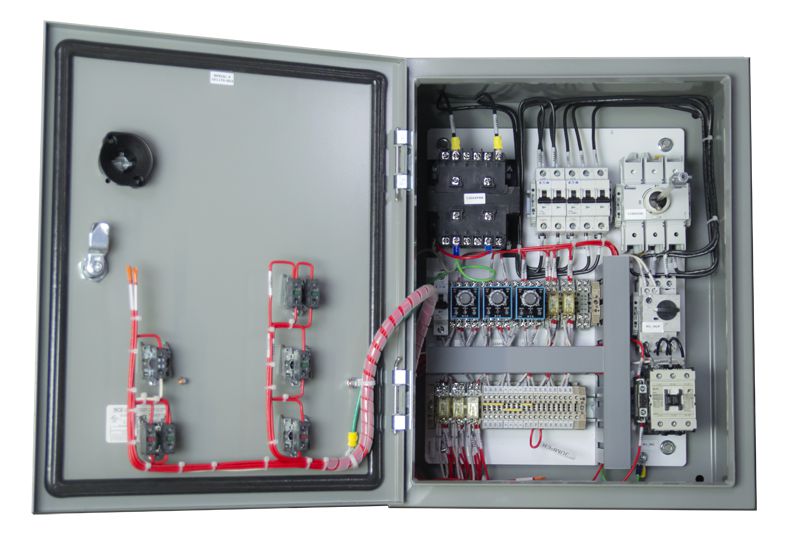
Motor Starter Panels
Motor starters are electromagnetically operated devices that start and stop a motor. This panel may contain one or more motor starters as well as selector switches or pushbuttons to control the motor, circuit protection, power distribution, and a power disconnect switch.
Pneumatic Control Panels
These control panels house pneumatic components that make up the control logic. Air is routed through components that determine the output of the controls.