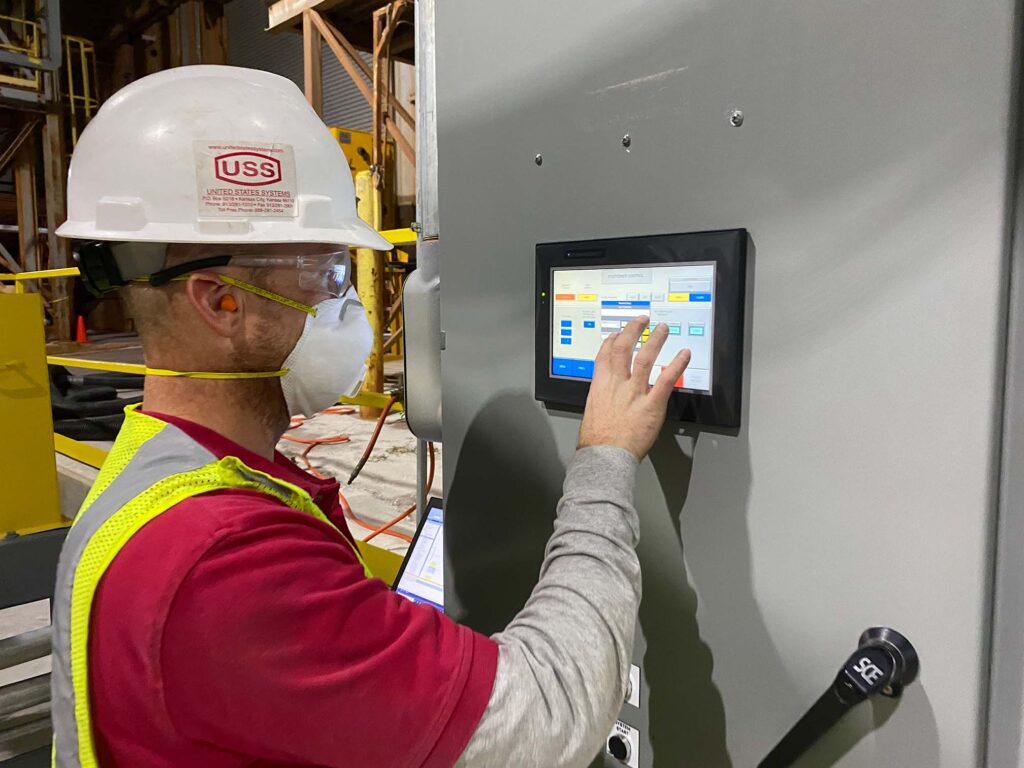
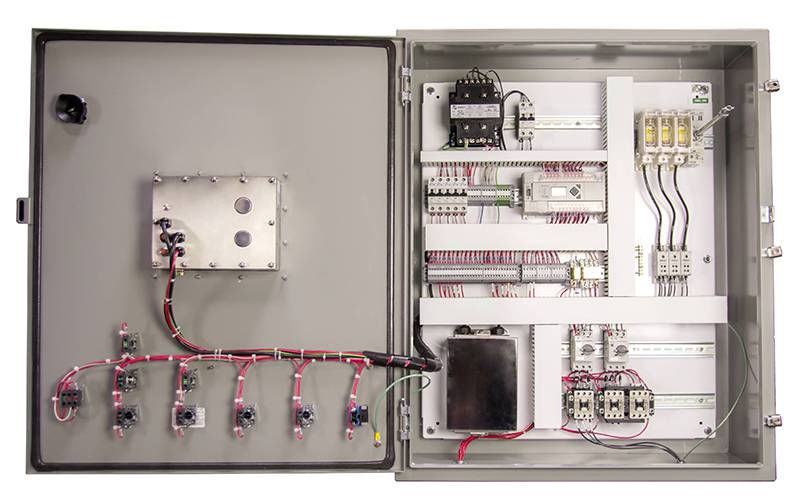
GET YOUR FACTORY MOVING
PLC PROGRAMMING
HMI PROGRAMMING
CONTROL PANEL DESIGN
INSTRUMENT SELECTION
CONTROL PANEL FABRICATION
PLC RETROFITTING
HISTORIZATION & REPORTING
EMERGENCY RESPONSE
SCADA / SYSTEM INTEGRATION
SYSTEM UPGRADES
PREVENTATIVE MAINTENANCE
TROUBLESHOOTING & REPAIR
Our PLC programmers squeeze precious efficiency out of your operation.
Comprehensive Automation Expertise
We bring extensive experience in various areas of automation, ensuring your systems operate at peak performance and efficiency. Here’s a detailed look at our areas of expertise:
Our Expertise:
- PLC Programming: Our team excels in designing and implementing robust Programmable Logic Controller (PLC) solutions, automating complex industrial processes with precision and reliability.
- SCADA Design: We specialize in creating advanced Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition (SCADA) systems, providing real-time monitoring and control for industrial operations.
- HMI Development: Our Human-Machine Interface (HMI) solutions offer intuitive and user-friendly control interfaces, enhancing operator interaction with your systems.
- Historizing Data: We implement comprehensive data historization solutions, capturing and storing valuable process data for analysis and optimization.
- Industrial Reporting: Our reporting solutions provide detailed insights into your operations, helping you make informed decisions and improve performance.
- Industrial IT: We integrate cutting-edge IT solutions to enhance connectivity, security, and efficiency across your industrial environment.
As manufacturing facilities around the globe increasingly rely on PLCs, the technology continues to evolve. We stay at the forefront of these advancements, ensuring our expertise in developing, supporting, and managing these systems is second to none.
Tailored Solutions for Seamless Operations
We understand the critical importance of keeping your systems running smoothly. Our approach is customer-centric, meaning we listen to your needs and collaborate with you to design the perfect automation solution for your specific requirements. Our commitment to excellence has enabled us to assist clients with a wide range of tasks, including:
- Building Systems from the Ground Up: We design and implement complete automation systems for new facilities, ensuring they are equipped with the latest technologies for optimal performance.
- Retrofitting and Upgrading: We specialize in retrofitting new PLCs into existing systems without causing downtime, ensuring seamless transitions and minimal disruption to your operations.
Partner with us to experience the benefits of our extensive automation expertise, personalized service, and dedication to helping you achieve operational excellence. Let’s work together to create solutions that drive productivity, reliability, and success for your business.
Out with the Old, In with the New: A Case Study
A large worldwide chemicals firm that makes plastic pellets hired USS Automation for the important task of retrofitting new modern PLCs into a facility with four product lines controlled by one PLC each.
The PLCs had different characteristics from the old ones that we had to analyze and control for.
If anything didn’t work the moment we turned it on then the company would experience downtime so that was to be avoided.
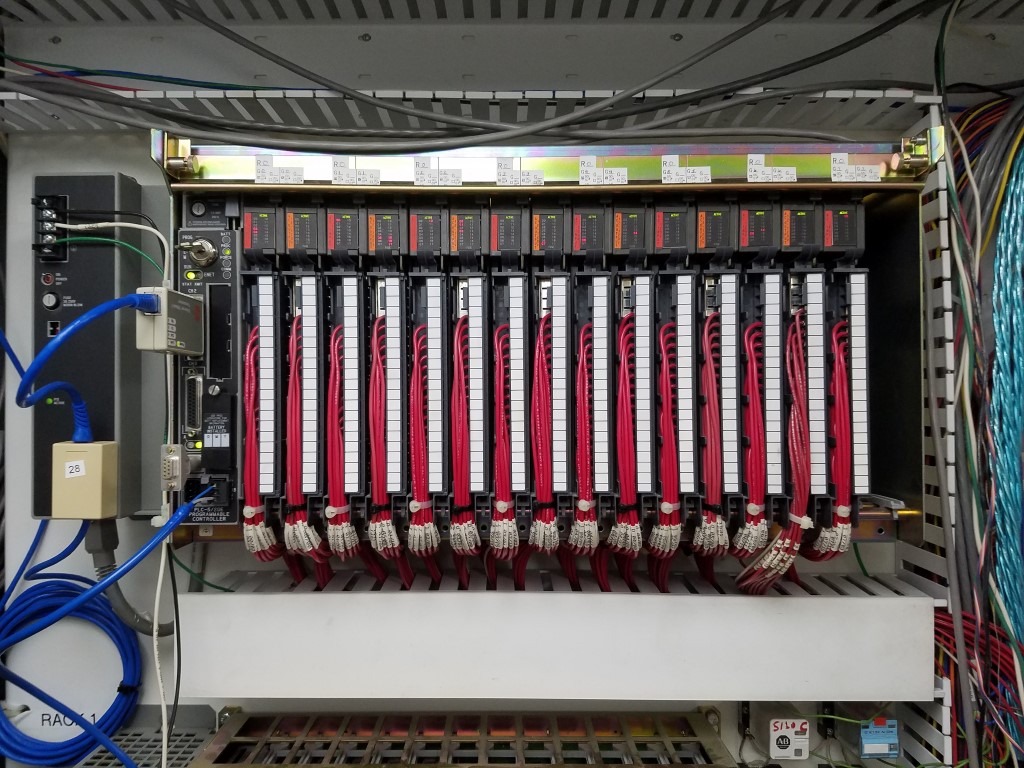
Old PLC:

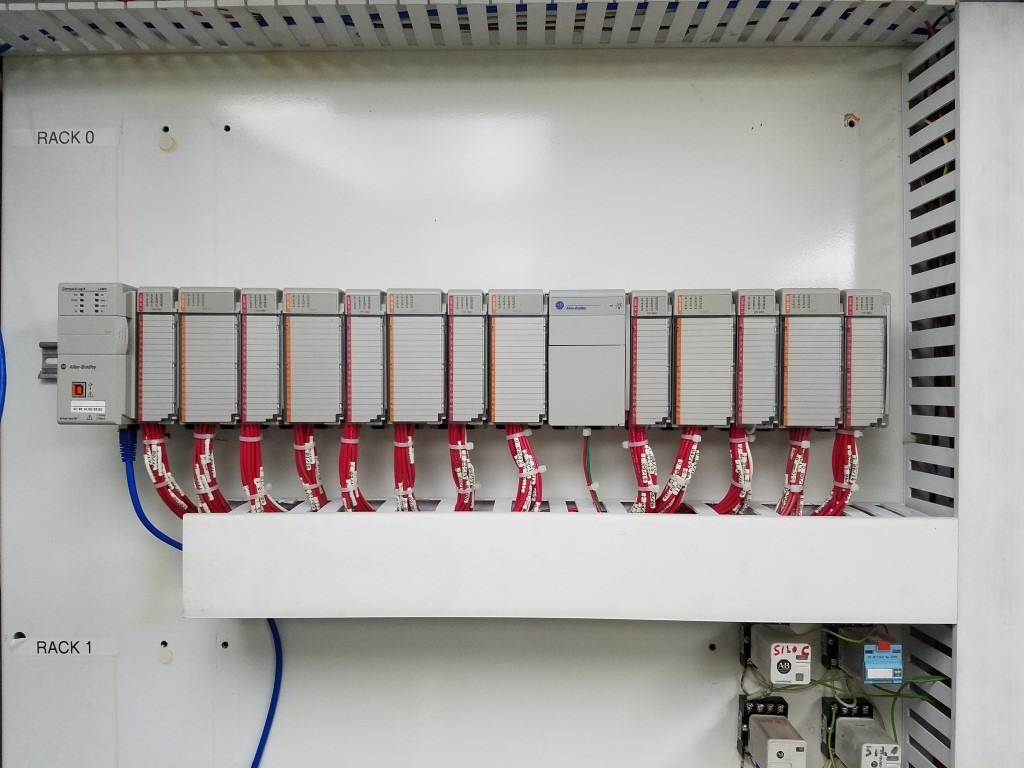
New PLC:

We were also tasked with giving their Wonderware InTouch software a makeover because a large number of links, animations, and graphics had deteriorated and weren’t working from various changes over the decades.
And it all had to be done without changing the underlying programming they use as the batching system to run their facility.
Any hiccup would result in downtime and lost revenue.
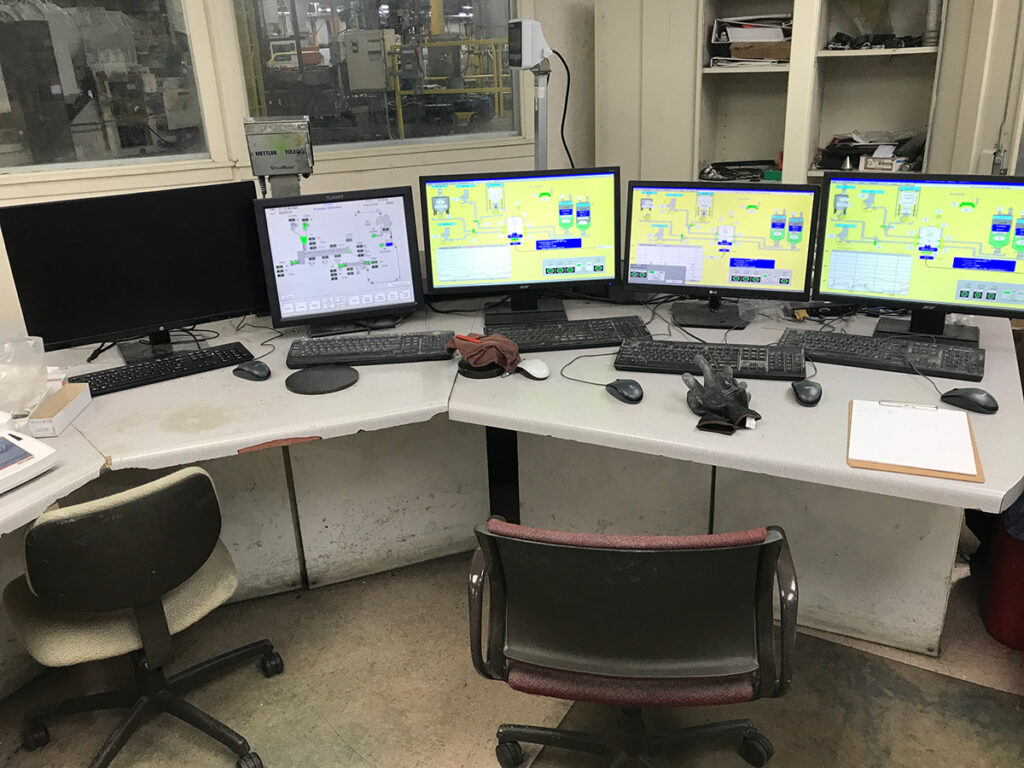

The customer also asked us to install Wonderware Historian to historize their processes. We also configured industrial reporting software so they can analyze the quality of their product.
Oh and in addition to replacing the PLCs we were replacing the PCs that ran the Wonderware systems as well.
This was a large, important project so we split up the effort between our team, began analysis, research, and went to work.
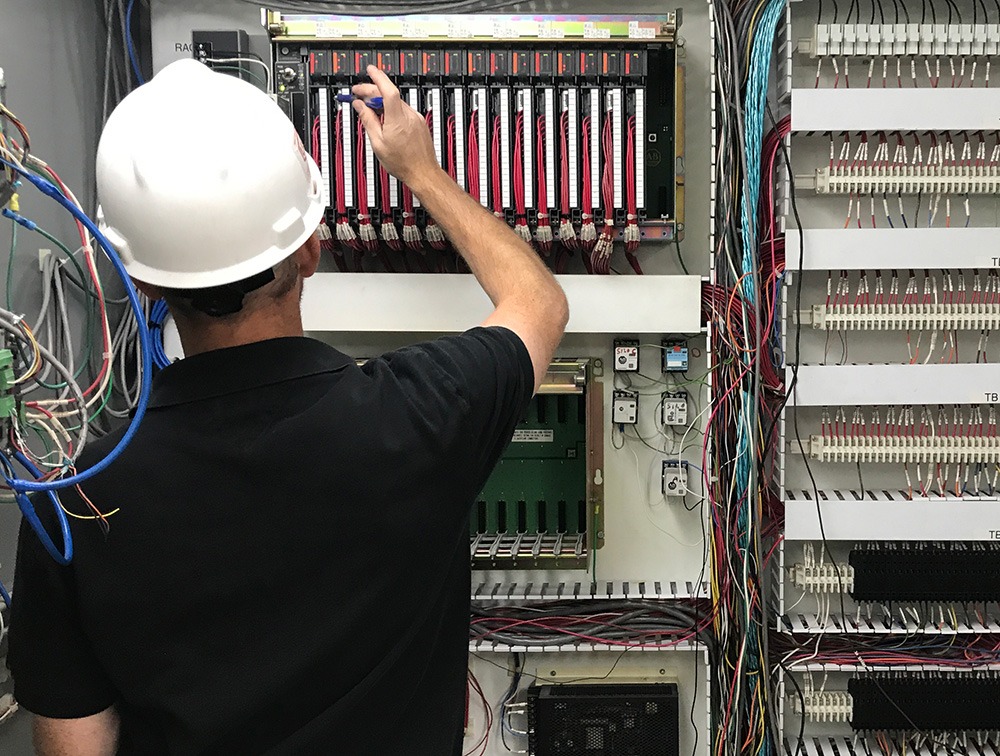

The effort paid off. Once the PLCs were programmed, the PCs were configured, the software refreshed, and the Historian was installed and configured we traveled to the facility to do the physical installation.
We performed the installation of the components over a long weekend while the plant was already in a pre-planned downtime state.
After removing and reconnecting thousands of wires, replacing the PLCs and PCs over the course of two days it was time to switch it on and work out anything else left to do.
We spent the next day getting the software perfected and the entire plant was up and running when the operators showed up for work the day after.
The result was ZERO plant downtime! The feedback from the operators was great…they loved the updated system and management did too.
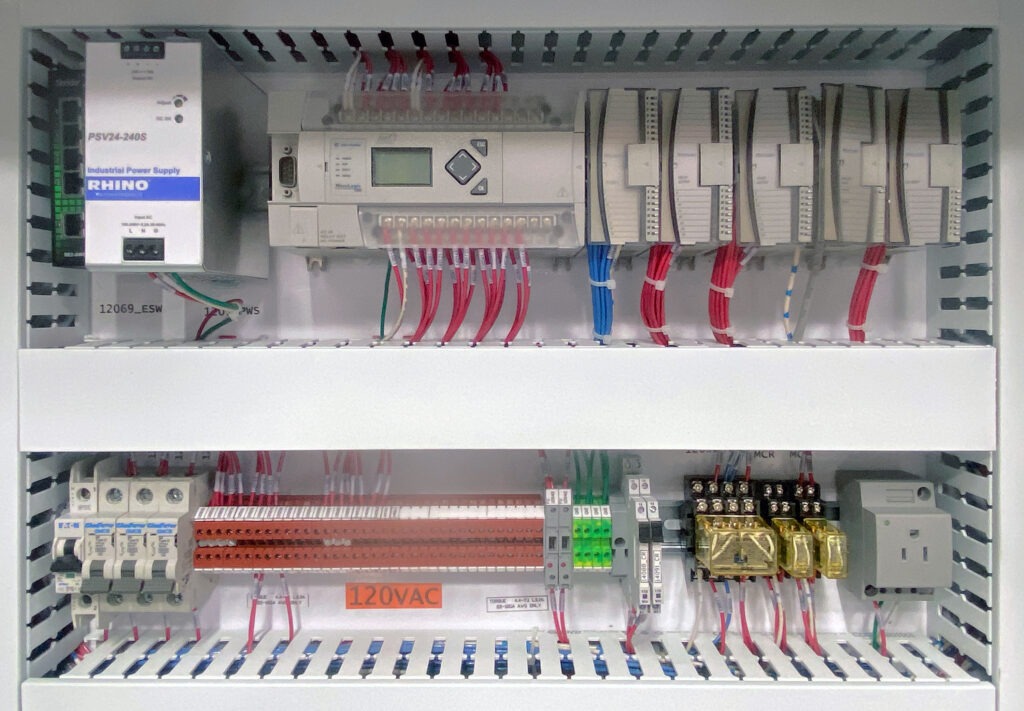
PLC Cabinet Before:
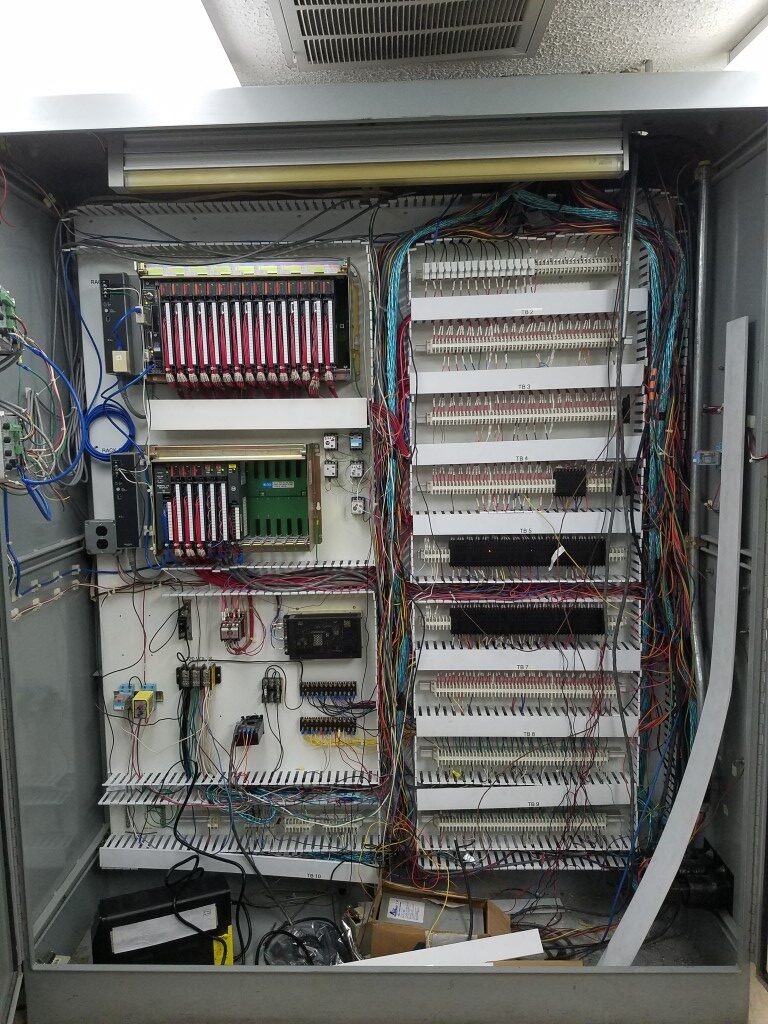
PLC Cabinet After:
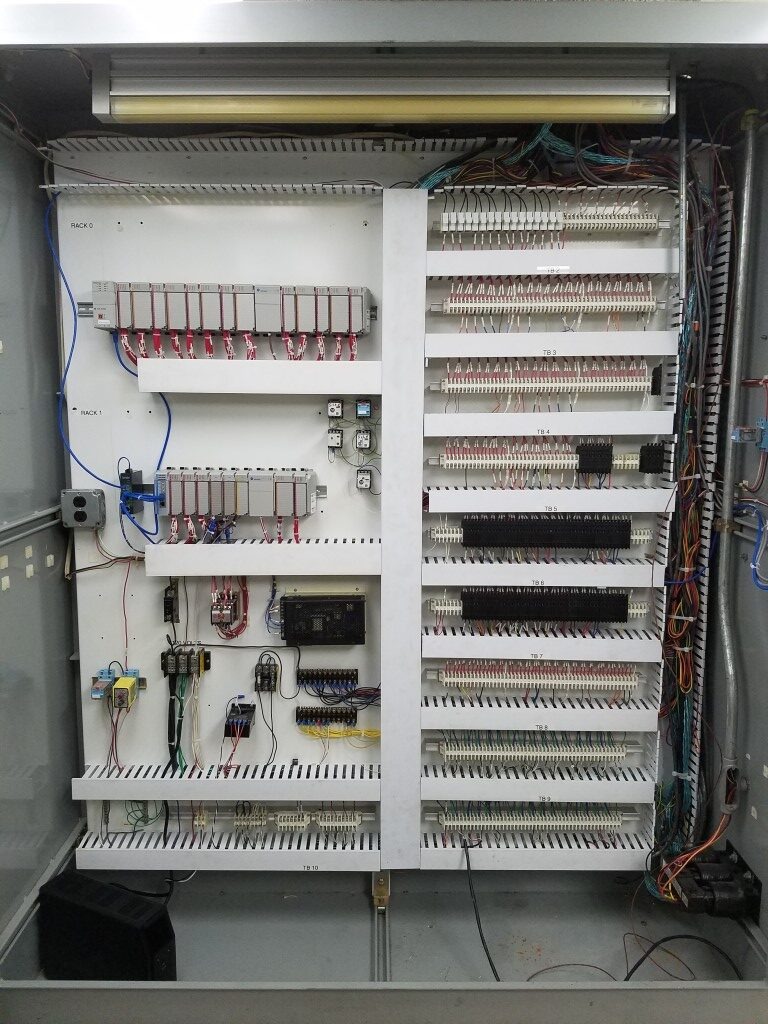
About Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs)
A Programmable Logic Controller (PLC) is an industrial digital computer designed to control manufacturing processes like assembly lines, robotic devices, and machinery. Its key features and functionalities make it essential for ensuring efficient and reliable industrial automation. Here’s what makes PLCs integral to modern industrial systems:
Key Features of PLCs
- Programmability: PLCs can be easily programmed to perform a wide range of tasks using ladder logic, a programming language that mimics electrical control circuits. This allows for customization to fit specific process or machine requirements.
- Real-Time Operation: Operating in real-time, PLCs process inputs and execute instructions almost instantly, maintaining precise control over manufacturing processes.
- Input and Output Modules: Equipped with various input and output modules, PLCs interface with machinery. Inputs include sensors and switches, while outputs control motors, valves, lights, and more.
- Robustness: Designed for harsh industrial environments, PLCs are built to be durable and reliable, handling extreme temperatures, humidity, vibration, and electrical noise.
- Connectivity: Modern PLCs feature communication capabilities that allow them to connect to Human-Machine Interfaces (HMIs), Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition (SCADA) systems, and IT networks, facilitating data collection and remote monitoring.
- Safety: Incorporating safety features like emergency stop functions, fail-safe states, and redundancy, PLCs ensure safe operations and prevent accidents and equipment damage.
How PLCs Work
- Scan Cycle: PLCs operate in a continuous loop called a scan cycle, during which they read inputs, process the program logic, and update outputs. This cycle repeats at high frequency, ensuring real-time control.
- Programming: Engineers create and upload programs to the PLC using software, defining how the PLC responds to various inputs and controls outputs. Common programming languages include ladder logic, Structured Text (ST), and Function Block Diagram (FBD).
- Control: Once programmed, the PLC continuously monitors inputs from sensors and devices, making decisions based on programmed logic and sending commands to output devices to control machinery and processes.
PLCs are pivotal in modern industrial automation, enhancing efficiency, consistency, and safety. They play a crucial role in optimizing various industrial processes, ensuring smooth and reliable operations.

Understanding SCADA: Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition
SCADA (Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition) systems are essential for industrial organizations seeking to maintain efficiency, process data for smarter decisions, and communicate system issues to help mitigate downtime. Here’s a closer look at what SCADA is and how it benefits your operations:
What is SCADA?
SCADA is an automation control system that enables organizations to monitor, gather, and process real-time data. It operates by interacting directly with devices such as sensors, valves, pumps, and motors through human-machine interface (HMI) software. SCADA systems provide a comprehensive control structure, ensuring smooth and efficient operation of complex industrial processes.
Key Components of SCADA Systems:
- HMI (Human-Machine Interface): This is the user interface that connects operators to the SCADA system, allowing them to interact with and control processes via graphical representations.
- RTUs (Remote Terminal Units): These are microprocessor-controlled devices that interface with physical equipment, collecting data and sending it to the central system.
- PLCs (Programmable Logic Controllers): Often used in place of RTUs, PLCs offer similar functionalities but with more sophisticated control and automation capabilities.
- Communication Infrastructure: This includes networks and communication protocols that facilitate data transfer between the SCADA central system and field devices.
- SCADA Software: The heart of the system, SCADA software processes data, generates reports, and triggers alarms when necessary.
Benefits of SCADA Systems:
- Real-Time Data Collection: SCADA systems provide immediate access to real-time data, enabling operators to make informed decisions and respond quickly to issues.
- Improved Efficiency: By automating data collection and control processes, SCADA systems enhance operational efficiency and reduce the likelihood of human error.
- Predictive Maintenance: With continuous monitoring, SCADA systems can predict and highlight maintenance needs before they become critical, reducing downtime and repair costs.
- Increased Productivity: Automation and efficient data processing lead to higher productivity by optimizing the use of resources and reducing operational delays.
- Scalability: SCADA systems can be scaled to meet the needs of any size operation, from small facilities to large, complex industrial environments.
Applications of SCADA:
SCADA systems are widely used across various industries, including:
- Manufacturing: For monitoring and controlling production processes.
- Energy: In power generation, transmission, and distribution.
- Water and Wastewater: For managing treatment plants and distribution networks.
- Transportation: To control traffic signals, manage railway networks, and monitor infrastructure.
- Oil and Gas: For drilling, production, and pipeline monitoring.
In essence, SCADA systems are the backbone of modern industrial automation, providing critical oversight and control that drive efficiency, productivity, and profitability.